Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 11th Computer Applications Guide Pdf Chapter 6 Word Processor Basics (OpenOffice Writer) Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 11th Computer Applications Solutions Chapter 6 Word Processor Basics (OpenOffice Writer)
11th Computer Applications Guide Introduction to Computers Text Book Questions and Answers
Part – I
Choose The Correct Answers
![]()
Question 1.
Which is the opening screen of OpenOffice?
a) Star desktop
b) Star center
c) Star screen
d) Star window
Answer:
b) Star center
Question 2.
Which option allows you to assign text, tables, graphics and other items to a key or key combination?
a) Autoformat
b) Automatic
c) Auto text
d) Autographies
Answer:
c) Auto text
Question 3.
Which menu contains the Numbering option?
a) File
b) Edit
c) Tools
d) Format
Answer:
d) Format
Question 4.
Which is displayed at the top most part of the window?
a) Menu bar
b) Tool bar
c) Title bar
d) Format bar
Answer:
c) Title bar
Question 5.
Which is changing the default appearance of the text called?
a) Text formatting
b) Page formatting
c) Special formatting
d) Paragraph formatting
Answer:
a) Text formatting
Question 6.
The Find & Replace option is available in which menu?
a) File
b) Edit
c) Format
d) Tools
Answer:
b) Edit
Question 7.
Which button selects all instances of the search text in the document?
a) Find
b) Find All
c) Replace
d) Replace All
Answer:
b) Find All
Question 8.
What is the shortcut key to go to the start of the document?
a) Ctrl + Home
b) Ctrl + End
c) Home
d) End
Answer:
a) Ctrl + Home
Question 9.
What is the shortcut key for finding and replacing text in a document?
a) Ctrl + F
b) Ctrl + F4
c) Ctrl + F5
d) Ctrl + F7
Answer:
a) Ctrl + F
Question 10.
What is the short cut key for Undo?
a) Ctrl +E
b) Ctrl + U
c) Ctrl + Z
d) Ctrl + n
Answer:
c) Ctrl + Z
Part – II
Very Short Answers
Question 1.
How do you insert pictures in to your document?
Answer:
To insert an image/picture from a file, the steps are as follows:
- Place the insertion pointer where you want the image to appear
- Select Insert → Picture From file
- The insert picture dialog box appears where the picture gallery opens from which the desired picture can be selected.
- If the picture is not in the gallery, then browse the pictures from the folder, choose the desired one and
- Click on the Open button
- The selected picture is inserted into the document.
![]()
Question 2.
What are the different packages in OpenOffice writer?
Answer:
OpenOffice is a productive office suite with a collection of different software packages such as –
- OpenOffice Writer – Word Processor to create text documents
- OpenOffice Calc – Spreadsheet to create worksheets
- OpenOffice Base – Database
- OpenOffice Impress – Presentation software
- OpenOffice Draw – Drawing Software
- OpenOffice Formula – Create formula and equations
Question 3.
What is auto text in writer?
Answer:
Auto Text allows you to assign text, tables, graphics and other items to a key or key combination. For example, rather than typing “TamilNadu” every time you use that phrase, you might just type “tn” and press F3.
Question 4.
How do you merge ceils in a table?
Answer:
To merge a group of cells:
- Select the cells to merge.
- Right click and choose Cell → Merge or choose Table → Merge Cells from the menu bar.
Question 5.
State the difference between proprietary software and open source software?
Answer:
Proprietary Software:
- It is closed source software that means the company who developed the software owns it and others can not duplicate or distribute it without permission.
- User have to pay and use.
- Example : Windows, Adobe Photoshop.
Open Source Software:
- It provides source code for the users and the user can modify if they want according to their requirement.
- It is a software which is free to use.
- Example : Linux, Open office.
Part – III
Short Answers
Question 1.
What is the difference between moving and copying text?
Answer:
Copy Text:
- Copy text will leave the source as it is and place a copy in the destination.
- After copy, the text available in both source and destination locations.
Move Text:
- Move text will shift the source to the destination i.e., the text will change its position.
- After move, the text available in destination location alone.
Question 2.
What are the different types of orientation?
Answer:
Page orientation refers to how the document will be displayed on screen and printed. There are two different orientations:
Landscape : The width of the document is more than the height. This is best suited for displaying professional photos, invitations, albums, tables etc.

Portrait : This is the most common and default orientation. Here, the height of the document is more than the width. Normally books, newspapers will be displayed in this format.

Question 3.
How do you insert rows and columns?
Answer:
To insert rows or columns inside a table:
1. Place the insertion pointer in the row or in the column where you would like to add new rows or columns and right-click.
2. Choose Row → Insert – to insert a row or Column → Insert – to insert a column. A dialog box will appear, from which we can select the number of rows or columns to insert. We can also set the position of the new rows or columns to Before or After as shown in the following Figure.
3. Click OK to close the dialog box.

Question 4.
What are the different ways to save a document?
Answer:
Saving the Document:
The first time the document is saved, OpenOffice Writer prompts for a name. Naming the file enables the user to find and open that file again. One can select the drive and folder where the file will be stored. To save a document for a first time, the following steps are used:
- Click File → Save → (or) File Save As (or) press Ctrl + S
- The “Save As” dialog box appears
- Select location to store your document. The default location to store all documents is “Documents” folder in Windows.
- Type your document name in the File Name box.
- All documents in OpenOffice writer will be stored with .odt extension.
- Finally, Click “Save” button.
- Once the file is saved, our document name will be displayed on the title bar.
Save as Microsoft Word document or PDF : We can store our OpenOffice document as Microsoft Word document or pdf. To do so, select file type from Save as type list box. This list box shows variety of formats to be saved.
Saving with password : In OpenOffice writer, a document can be protected with a password. We can set a password to protect your document while saving a file. To save a file with password, click on “Save with Password” check box and then click “Save” button. Immediately it shows “Set Password” dialog box as given in the following Figure.

In this dialog box, Enter a password in “Enter Password to open” text box and retype the same password in “Confirm Password” box for confirmation. Finally click “OK” button.
Save document as Read only:
We can save the document as read only i.e. editing is not possible by using More Option.
Question 5.
Write the steps to change the line spacing of text.
Answer:
Line spacing determines the amount of vertical space between lines of text in a paragraph. By default, the lines are single-spaced, that is the spacing accommodates the largest font in that line, plus a small amount of extra space.
Method – 1
Select the line or word or phrase, Right-click Line spacing, then select the required type as single, 1.5 or double
Method – 2
- Select the entire document by Edit → Select All
- Format → Paragraph
- The paragraph dialog box appears, click Indents & Spacing tab.
- In the line spacing option, select the type and click OK button.
Part – IV
Explain In Brief
Question 1.
What are the different methods to change margin in writer?
Answer:
Changing or setting page margins in Open office writer can be done in two ways:
- Using the Rulers – quick and easy, but does not have precise values.
- Using the Page Style dialog box – can specify precise values for the margins.
Changing page margins – using Ruler:
- The shaded sections of the rulers are the margins.
- Hold the mouse pointer over the line between the gray and white sections.
- The mouse pointer turns into a double¬headed arrow.
- Hold down the left mouse button and drag the mouse to move the margin and release it at the required point.
- The new margin is set.
Changing Margins using the Page Style dialog box
- Right-click anywhere on the page and select Page from the popup menu and select page tab of page style dialog box.
- In the Margins boxes, specify the values for left , right, top and bottom margins.
- Click on ok button.
![]()
Question 2.
What are Header and Footer? How do you Insert page numbers?
Answer:
The header is a section of the document that appears in the top margin, which displays the title or chapter name, author name of a document. The footer is a section of the document that appears in the bottom margin of the page which displays the page number, date, time etc. which gets displayed on ail the pages automatically.
Inserting Header and Footer
- Select Insert → Header → Default from the main menu.
- The header text area is separated from the normal text area.
- In the header area, Enter the text that is to be repeated in all pages or Select Insert → Fields → Title.
Similarly to insert a Footer, the steps are as given below:
- Select Insert → Footer → Default from the main menu.
- Place the insertion pointer in the footer part of the page.
- Select Insert Fields → Date to insert date in all the page
Once the headers and footers are given in the first page, the same text appears in all the pages.
Inserting and Formatting page numbers – Once the Header / Footer area is enabled, the page numbers can be inserted by performing the following steps:
- position the insertion pointer where you want to insert the page number
- choose Insert → Fields Page Number
- The page number appears with a gray background.
Normally, the page numbers appear as 1, 2, 3, …., To change the numbering style, the following sequence of steps can be performed:
- Position the cursor where the page number has to appear.
- Select Format Page, which will bring the page style dialog box.
- Select Page Tab.
- In the Layout settings, select the format drop down combo box.
- Select the desired style and click OK button.
Question 3.
Write the steps to Find and Replace a word with another word in Open Office writer?
Answer:
OpenOffice Writer has a Find and Replace feature that helps to locate for a text inside a document and replace it with another word. In addition to finding and replacing words and phrases, we can also use wildcards and regular expressions to perform advanced search. To search a word:
1. Click Edit → Find & Replace (or) Ctrl + F
2. The Find & Replace dialog box appears as shown below.

Steps to And & replace a text:
1. Type the text you want to find in the Search for box
For Example: To search a word “Bombay” in a document and replace with “Mumbai”, enter the word “Bombay” in the Search for box.
2. To replace the text with different text, type the new text in the Replace with box Enter the word “Mumbai” in the Replace with box and Click Find button , to start the search , the found word is highlighted and the first occurrence of “Bombay” is highlighted.
3. To replace text, click Replace button.
The highlighted word is replaced with the word given in the replace with box.
4. Click Find All, Writer selects all instances of the search text in the document.
All occurrences of Bombay are highlighted.
5. Click Replace AH button, Writer replaces all matches.
This will replace all occurrences of “Bombay” with “Mumbai”.
6. Enable Match case to perform the search case sensitively so that uppercase and lower cases are distinguished separately.
7. Enable Whole Words only to make the search more specific to words used separately alone.
Question 4.
Explain Page formatting in writer.
Answer:
The most important thing in a word processor is how to format the page with elements such as margins, numbering, page layout, headers and footers. Formatting our pages makes them look more attractive and makes them easier to read.
Setting the Page Size and Margins – Changing Page Size:
The default page size in writer is 8.5 x 11″, the same as that of a standard A4 printing paper. However, for different types of documents, you may need to change the page size.
Changing page margins:
Page margins are the white space around the top, bottom, left, and right of your document. Margins . let Writer know where to start placing the text at the top of a document, when to move on to the next page at the bottom, where to start typing text on the left side, and where to stop and move to the next line on the right.
Changing or setting page margins in Open office writer can be done in two ways:
- Using the Rulers – quick and easy, but does not have precise values.
- Using the Page Style dialog box – can specify precise values for the margins.
Page Orientation:
Page orientation refers to how the document will be displayed on screen and printed. There are two different orientations:
Landscape :
The width of the document is more than the height. This is best suited for displaying professional photos, invitations, albums, tables etc.

Portrait:
This is the most common and default orientation. Here, the height of the document is more than the width. Normally books, newspapers will be displayed in this format.

Changing the page color is not quite common. To do so, in the Page style dialog box, select Background tab, In As option click on color and select the “color” from the color palette or select “graphic” to apply an image as a page background Borders can be applied to an entire document, an entire page, paragraph, or just to certain sections of the document. From the page style dialog box, select the Border tab, the user defined area helps to define the area of borders, the line style of borders, color of borders can be selected.
Header and Footer:
The header is a section of the document that appears in the top margin, which displays the title or chapter name, author name of a document. The footer is a section of the document that appears in the bottom margin of the page which displays the page number, date, time etc. which gets displayed on all the pages automatically.
![]()
11th Computer Applications Guide Word Processor Basics (OpenOffice Writer) Additional Important Questions and Answers
Part – I
Choose The Correct Answers:
Question 1.
_______ is computer software to create, edit, manipulate, transmit, store and retrieve a text document.
a) Word processor
b) Word processing
c) Text processor
d) Spreadsheet
Answer:
a) Word processor
Question 2.
_______ is an activity carried out by a computer with suitable software to create, edit, manipulate, transmit, store and retrieve text documents.
a) Word processor
b) Word processing
c) Text processor
d) Spreadsheet
Answer:
b) Word processing
Question 3.
_______ is word processing activity.
a) Word processor
b) Word processing
c) Text processor
d) Spreadsheet
Answer:
d) Spreadsheet
Question 4.
_______ is a proprietary source word processing software.
a) Microsoft Word
b) WPS Word
c) WordPro
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 5.
_______ is a open source word processing software
a) Open Office Writer
b) LibreOffice Writer
c) Abiword
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 6.
Who is the developer of Microsoft Word?
a) Microsoft Corporation
b) Kingsoft
c) Lotus Corporation
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Microsoft Corporation
Question 7.
Who is the developer of WPS Word?
a) Microsoft Corporation
b) Kingsoft
c) Lotus Corporation
d) None of these
Answer:
b) Kingsoft
Question 8.
Who is the developer of WordPro?
a) Microsoft Corporation
b) Kingsoft
c) Lotus Corporation
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Lotus Corporation
![]()
Question 9.
Who is the developer of Open Office Writer?
a) Apache
b) The document foundation
c) Abisource
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Apache
Question 10.
Who is the developer of LibreOffice Writer?
a) Apache
b) The document foundation
c) Abisource
d) None of these
Answer:
b) The document foundation
Question 11.
Who is the developer of Abiword?
a) Apache
b) The document foundation
c) Abisource
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Abisource
Question 12.
Identify the odd one from the following.
a) Open Office Writer
b) LibreOffice Writer
c) Abiword
d) WordPro
Answer:
d) WordPro
Question 13.
Identify the odd one from the following.
a) Apache
b) The document foundation
c) Abisource
d) Lotus Corporation
Answer:
d) Lotus Corporation
Question 14.
Identify the odd one from the following.
a) OpenOffice Writer
b) OpenOffice Calc
c) OpenOffice Formula
d) OpenOffice Draw
Answer:
d) OpenOffice Draw
Question 15.
_______ is a Tamil word processor.
a) Tamil Openoffice Writer
b) Mentamiz 2017
c) Kamban 3.0
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
![]()
Question 16.
_______ is a familiar word processors exclusively for Tamil Language.
a) Tamil Openoffice Writer
b) Mentamiz 2017
c) Kamban 3.0
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 17.
_______ provides full Tamil interface to its office suits.
a) Borland International
b) Microsoft
c) Apple
d) None of these
Answer:
b) Microsoft
Question 18.
_______ stores all our data in an International open standard format.
a) Microsoft Office
b) Open Office
c) Kamban 3.0
d) None of these
Answer:
b) Open Office
Question 19.
________ can read and write files from other common office software packages.
a) Microsoft Office
b) Open Office
c) Kamban 3.0
d) None of these
Answer:
b) Open Office
Question 20.
________ is available in many languages and works on all common computers.
a) Microsoft Office
a) OpenOffice Writer
c) Kamban 3.0
d) None of these
Answer:
a) OpenOffice Writer
Question 21.
_______ is a word processor of OpenOffice.
a) OpenOffice Writer
b) OpenOffice Calc
c) OpenOffice Formula
d) OpenOffice Impress
Answer:
a) OpenOffice Writer
Question 22.
_______ is a spreadsheed of OpenOffice.
a) OpenOffice Writer
b) OpenOffice Calc
c) OpenOffice Formula
d) OpenOffice Impress
Answer:
b) OpenOffice Calc
Question 23.
________ is a database of OpenOffice.
a) OpenOffice Base
b) OpenOffice Calc
c) OpenOffice Formula
d) OpenOffice Impress
Answer:
d) OpenOffice Impress
Question 25.
_______ is a presentation application of OpenOffice.
a) OpenOffice Writer
b) OpenOffice Calc
c) OpenOffice Formula
d) OpenOffice Impress
Answer:
d) OpenOffice Impress
Question 26.
________ application of OpenOffice is used to create formula and equations.
a) OpenOffice Writer
b) OpenOffice Calc
c) OpenOffice Formula
d) OpenOffice Impress
Answer:
c) OpenOffice Formula
Question 27.
________ is the usual feature of a word processor.
a) Spell check
b) Thesaurus
c) Hyphenation
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 28.
_______ is the usual feature of a word processor.
a) Find and Replace
b) Mail Merge
c) Automatic generation of tables of content
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 29.
________ is the important feature of a word processor.
a) Templates and Styles
b) Page layout methods
c) Embedding of other objects
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
![]()
Question 30.
________ is the important feature of a word processor.
a) Database integration
b) Export to PDF
c) Built-in Drawing tools
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 31.
PDF stands for _______.
a) Portable Document Format
b) Printable Data Format
c) Pioneer Data Format
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Portable Document Format
Question 32.
The opening screen of OpenOffice is called as _______.
a) Star Center
b) Open Center
c) Work Center
d) Document Center
Answer:
a) Star Center
Question 33.
________ is the shortcut key to open new text document.
a) Ctrl + N
b) Alt+N
c) Shift + N
d) Esc + N
Answer:
a) Ctrl + N
Question 34.
The is displayed at the top most part _______ of the window.
a) Menu bar
b) Title bar
c) Scroll bar
d) None of these
Answer:
b) Title bar
Question 35.
_______ displays the name of the document and the name of the application.
a) Menu bar
b) Title bar
c) Scroll bar
d) None of these
Answer:
b) Title bar
Question 36.
By default, the initial document is given the name as _______.
a) Untitled
b) Document
c) Nonamet
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Untitled
Question 37.
In the right corner of title bar _______ control button is available
a) minimize
b) maximize/restore
c) close
d) all the above
Answer:
d) all the above
Question 38.
When we click ________ button, it shrinks our document window smaller in size and shows it as a small button on the task bar.
a) minimize
b) maximize/restore
c) close
d) all the above
Answer:
a) minimize
Question 39.
When we click ________ button, our document window is displayed in full screen.
a) minimize
b) maximize
c) close
d) restore
Answer:
b) maximize
Question 40.
When the window is in full screen, the maximize button is changed as _______.
a) maximize
b) close
c) restore
d) none of these
Answer:
c) restore
Question 41.
When we click _______ button, the document window regains its original size.
a) maximize
b) close
c) restore
d) minimize
Answer:
c) restore
Question 42.
When we click ______ button, the application is closed and OpenOffice returns back to the desktop.
a) maximize
b) close
c) restore
d) minimize
Answer:
b) close
Question 43.
The close button may be called as _______
a) Exit
b) Quit
c) Either A or B
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Either A or B
![]()
Question 44.
The _______ is just below the title bar which comprises of various menus consisting of various options.
a) Menu bar
b) Tool bar
c) Scroll bar
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Menu bar
Question 45.
The _______ menu contains various option for file management task.
a) File
b) Format
c) Edit
d) Tools
Answer:
a) File
Question 46.
_______ is the File menu option.
a) New / Open / Close
b) Save / Save As
c) Print / Export
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 47.
The Edit menu contains the editing option _______.
a) cut/ copy and paste
b) Undo
c) Find and Replace
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 48.
The _______ menu contains the options which are used to modify the environment of writer.
a) File
b) Format
c) Edit
d) View
Answer:
d) View
Question 49.
________ is a View menu option.
a) Navigator
b) Web layout
c) Print layout
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 50.
The _______ menu contains commands for inserting various elements.
a) Insert
b) Tools
c) Add
d) Elements
Answer:
a) Insert
Question 51.
________ is the Insert menu option.
a) Picture
b) Tables/Charts
c) Header / Footer
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 52.
The _______ menu contains the options of various text and page formatting features
a) File
b) Format
c) Edit
d) View
Answer:
b) Format
Question 53.
_______ is a Format menu option.
a) Bullets and Numbering
b) Font
c) Layout
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 54.
The _______ menu contains various tools to manage and manipulate tables.
a) File
b) Table
c) Insert
d) View
Answer:
b) Table
Question 55.
The Tools menu contains _______.
a) Mail merge
b) Spelling and Grammar
c) Endnotes/Footnotes
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 56.
The _______ menu shows display options such as New Window, Close Windows, Split and Freeze.
a) Window
b) File
c) Insert
d) View
Answer:
a) Window
Question 57.
The _______ menu lists out the inbuilt help features available with OpenOffice.
a) Window
b) File
c) Insert
d) Help
Answer:
d) Help
Question 58.
Under the menu bar, there are two _______ available by default.
a) toolbars
b) scroll bars
c) both a and b
d) none of these
Answer:
a) toolbars
Question 59.
Under the menu bar, _______ toolbar is available by default.
a) Standard
b) Formatting
c) Insert Object
d) Both A and B
Answer:
d) Both A and B
![]()
Question 60.
_______ tool bar consists of shortcut icons for frequently performed tasks.
a) Standard
b) Formatting
c) Insert Object
d) Both A and B
Answer:
a) Standard
Question 61.
_______ toolbar consists of icons used for formatting the text like bold, underline, italics, font type, font color.
a) Standard
b) Formatting
c) Insert Object
d) Both A and B
Answer:
b) Formatting
Question 62.
The _______ is a scale below the formatting tool bar which shows the margins.
a) ruler
b) tab stops
c) margin guide
d) none of these
Answer:
a) ruler
Question 63.
There are _______ set of rulers.
a) three
b) two
c) only one
d) no ruler
Answer:
b) two
Question 64.
_______ is a ruler type.
a) Horizontal Ruler
b) Vertical Ruler
c) Both A and B
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Both A and B
Question 65.
_______ ruler is used to set left and right margins of a page.
a) Horizontal Ruler
b) Vertical Ruler
c) Both A and B
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Horizontal Ruler
Question 66.
______ ruler is used to set top and bottom margins of a page.
a) Horizontal Ruler
b) Vertical Ruler
c) Both A and B
d) None of these
Answer:
b) Vertical Ruler
Question 67.
The _______ is the blank area which is used to type the content of the file.
a) work space
b) document space
c) window
d) none of these
Answer:
a) work space
Question 68.
A flashing vertical bar appears at the beginning of the screen which is called as _____
a) cursor
b) insertion point
c) Indicator
d) none of these
Answer:
b) insertion point
Question 69.
The ______ bar is at the bottom of the window.
a) status
b) scroll
c) tool
d) menu
Answer:
a) status
Question 70.
_______ bar shows the current status of the document such as number of pages, current page number, default language etc.
a) status
b) scroll
c) tool
d) menu
Answer:
a) status
![]()
Question 71.
When the text reaches the end of the line, the word is automatically wrapped to the next line is known as ________
a) Hard return
b) Soft return
c) Word wrap
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Word wrap
Question 72.
The _______ key must not be pressed at the end of the each line.
a) Enter
b) Tab
c) Backspace
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Enter
Question 73.
The Enter key should be pressed only ______
a) at the end of a paragraph
b) when a blank line is to be inserted
c) Either A or B
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Either A or B
Question 74.
______ key is used to move the insertion point to one word right.
a) Ctrl + →
b) Ctrl + ←
c) Ctrl + ↑
d) Ctrl + ↓
Answer:
a) Ctrl + →
Question 75.
________ key is used to move the insertion point to one word left.
a) Ctrl + →
b) Ctrl + ←
c) Ctrl + ↑
d) Ctrl + ↓
Answer:
b) Ctrl + ←
Question 76.
_______ key Ii used to move the insertion point to one paragraph up.
a) Ctrl + →
b) Ctrl + ←
c) Ctrl + ↑
d) Ctrl + ↓
Answer:
c) Ctrl + ↑
Question 77.
_____ key Is used to move the Insertion point to one paragraph down.
a) Ctrl + →
b) CtrI + ←
c) Ctrl + ↑
d) Ctrl + ↓
Answer:
d) Ctrl + ↓
Question 78.
_______ key Is us.d to move the Insertion
point to the beginning of a line.
a) Ctrl + Home
b) Ctrl + End
c) Home
d) End
Answer:
c) Home
Question 79.
________ key Is used to move the Insertion point to the end of a line.
a) Ctrl + Home
b) Ctrl + End
c) Home
d) End
Answer:
d) End
Question 80.
_______ key Is used to move the insertion point to the beginning of document.
a) Ctrl + Home
b) Ctrl + End
c) Home
d) End
Answer:
a) Ctrl + Home
Question 81.
________ key Is used to move the insertion point to the end of document.
a) Ctrl + Home
b) Ctrl + End
c) Home
d) End
Answer:
b) Ctrl + End
![]()
Question 82.
_______ key Is used to move the insertion point to one cell light.
a) Tab
b) Shift + Tab
c) PgUp
d) PgDn
Answer:
a) Tab
Question 83.
______ key Is used to move the insertion point to one cell left.
a) Tab
b) Shift + Tab
c) PgUp
d) PgDn
Answer:
b) Shift + Tab
Question 84.
_______ key Is used to scroll one screen up.
a) Tab
b) Shift + Tab
c) PgUp
d) PgDn
Answer:
c) PgUp
Question 85.
_______ key is used to scroll one screen down.
a) Tab
b) Shift + Tab
c) PgUp
d) PgDn
Answer:
d) PgDn
Question 86.
______ is the shortcut key to save a document.
a) ctrl+S
b) Ctrl+F
c) Alt+S
d) Shift+S
Answer:
a) ctrl+S
Question 87.
_______ check box s available in Save As dialog box.
a) Automatic file name extension
b) Save with password
c) Edit filter settings
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 88.
______ is the file extension for Open office writer flic.
a) odt
b) doc
c) docx
d) all the above
Answer:
a) odt
Question 89.
When the work Ii finished, we should save the document and then close document using _______.
a) File – Close command
b) Press Ctrl+W
c) Either A or B
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Either A or B
Question 90.
When we dose en unsaved file using the dose control button, select ______ from Alert Message box to accept the warning message.
a) Save
b) Discard
c) Cancel
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Save
Question 91.
When we close an unsaved file. using the close control button, select _______ from Alert Message box if we are not willing to save the file.
a) Save
b) Discard
c) Cancel
d) None of these
Answer:
b) Discard
Question 92.
When we close an unsaved file using the close control button, select ______ from Alert Message box if we want to cancel this warning and continue working in the same document.
a) Save
b) Discard
c) Cancel
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Cancel
Question 93.
_____ lithe shortcut key to open a document.
a) Ctrl + O
b) Ctrl + N
c) Ctrl + F
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Ctrl + O
Question 94.
Typing in Tamil has ______ methods.
a) 2
b) 3
c) 4
d) 5
Answer:
a) 2
Question 95.
________ is a Tamil typing method.
a) Using Tamil font
b) Using Tamil interface
c) Both A and B
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Both A and B
Question 96.
________ is a drawback of using Tamil font to Tamil text.
a) The user must be aware of Tamil typing.
b) The particular font must be available In the system.
c) It does not support other languages including English.
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
![]()
Question 97.
_______ is a drawback of using Tamil font to Tamil text.
a) The computer accepts characters as symbols not as language.
b) It is not portable
c) Both A and B
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 98.
_______ is an advantage of using Tamil Interface to Tamil text.
a) It follows Unicode technique. Hence knowledge of Tamil typing Is not necessarly
b) It Is easy to type documents in Tamil In any word processor
c) Some of the Unicode fonts supports all Indian languages
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 99.
_______ ¡s a Ta mil Interface.
a) Murasu
b) NHM writer
c) both A and B
d) None of these
Answer:
c) both A and B
Question 100.
Once document s typed, corrections can be made In _______ ways.
a) 2
b) 3
c) 4
d) 5
Answer:
a) 2
Question 101.
Once document is typed, corrections can be made using _______ key.
a) Backspace
b) Delete
c) Insert
d) Either A or B
Answer:
d) Either A or B
Question 102.
________ key deletes the character left of the Insertion point.
a) Backspace
b) Delete
C) Insert
d) Either A or B
Answer:
a) Backspace
Question 103.
key deletes the character right of the Insertion point.
a) Backspace
b) Delete
c) Insert
d) Either A or B
Answer:
b) Delete
b) Delete
Question 104.
_______ is a text Insertion mode.
a) Insert mode
b) Type over mode
c) Both A and B
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Both A and B
Question 105.
We can toggle between the insert mode and type over mode by pressIng the _______ key.
a) Backspace
b) Delete
c) Insert
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Insert
Question 106.
Text selection can be done by methods.
a) two
b) three
c) four
d) only one
Answer:
a) two
Question 107.
_______ is text selection method.
a) Selecting the continuous text
b) Selecting the non continuous text.
c) both A and B
d) None of these
Answer:
c) both A and B
Question 108.
To select the text continuously, _______ key is used.
a) Shift
b) Ctrl
c) Alt
d) Esc
Answer:
b) Ctrl
Question 109.
To select the text non-continously, ________ key is used.
a) Shift
b) Ctrl
c) Alt
d) Esc
Answer:
b) Ctrl
![]()
Question 110.
The required text may be selected using _______.
a) Keyboard
b) Mouse
c) Shortcut key
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 111.
_______ helps to select the text quickly and easily.
a) Keyboard
b) Mouse
c) Shortcut key
d) All the above
Answer:
c) Shortcut key
Question 112.
_______ is a shortcut key to select a word.
a) Double click on the word
b) Ctrl + A
c) both A and B
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Double click on the word
Question 113.
_______ is a shortcut key to select the entire document.
a) Double click on the word
b) Ctrl + A
c) both A and B
d) None of these
Answer:
b) Ctrl + A
Question 114.
________ is used to cut the text.
a) Ctrl + X
b) Edit → Cut
c) Cut Icon
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 115.
________ is used to paste the text.
a) Ctrl + V
b) Edit → Paste
c) Paste Icon
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 116.
________ is used to copy the text.
a) Ctrl + C
b) Edit → Copy
c) Copy Icon
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 117.
_______ is used to Undo the operation.
a) Ctrl + Z
b) Edit Undo
c) Undo Icon
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 118.
_______ is used to open Paste Special dialog box.
a) Ctrl + Shift + V
b) Edit → Paste Special
c) Alt + E + S
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 119.
DDE means _______.
a) Dynamic Data Exchange
b) Data Dynamic Exchange
c) Direct Data Exchange
d) Dynamic Data Entry
Answer:
a) Dynamic Data Exchange
![]()
Question 120.
_______ is a mechanism whereby the source data can be pasted into the destination as a linked, ‘live’ copy of the original.
a) DDE link
b) Formatted text
c) Unformatted text
d) None of these
Answer:
a) DDE link
Question 121.
While paste the text with _______ option, any changes made in the source will immediately reflect into the destination.
a) DOE link
b) Formatted text
c) Unformatted text
d) None of these
Answer:
a) DOE link
Question 122.
_______ key Is used to open Help window In Open Office.
a) F1
b) Ctrl + F
c) Ctrl + F4
d) None of these
Answer:
a) F1
![]()
Question 123.
To activate ________ click Tools → Options → Open Office
a) Tooltips
b) Extended tips
c) The Help Agent
d) all the above
Answer:
a) Tooltips
Question 124.
For a more detailed explanation, select ________ and hold the mouse pointer over the icon where you want more help with.
a) Help → What’s This
b) Help → Content
c) Help → More
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Help → What’s This
Question 125.
A text without any special formatting gives a _______ appearance.
a) good
b) monotonous
c) contagious
d) None of these
Answer:
b) monotonous
Question 126.
________ is the most common types of text formatting.
a) Bold
b) Italic
c) Underline
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 127.
A ________ is a set of characters in a particular style.
a) font
b) paragraph
c) word
d) none of these
Answer:
a) font
Question 128.
Changing the default appearance of the text like changing the font type , size, color, style etc., are called as _______.
a) Text Editing
b) Text Formatting
c) Text
d) None of these
Answer:
b) Text Formatting
Question 129.
To make the text attractive and more appealing ________ is used.
a) Text Editing
b) Text Formatting
c) Text Processing
d) None of these
Answer:
b) Text Formatting
Question 130.
________ is the shortcut key to makes the text bold.
a) Ctrl + B
b) Ctrl + I
c) Ctrl + U
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Ctrl + B
Question 131.
________ is the shortcut key to underlines the text.
a) Ctrl + B
b) Ctrl + I
c) Ctrl + U
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Ctrl + U
Question 132.
________ is the shortcut key to italizes the text.
a) Ctrl + B
b) Ctrl + I
c) Ctrl + U
d) None of these
Answer:
b) Ctrl + I
![]()
Question 133.
The default font type is _______.
a) Times New Roman
b) Fajitha
c) Courier
d) Wingdings
Answer:
a) Times New Roman
Question 134.
The type of font can be changed by clicking on the – icon.
a) Font type
b) Font size
c) Font colour
d) all the above
Answer:
a) Font type
Question 135.
The font size can be changed by clicking on the – icon.
a) Font type
b) Font size
c) Font colour
d) all the above
Answer:
b) Font size
Question 136.
The font colour can be changed by clicking on the – icon.
a) Font type
b) Font size
c) Font colour
d) all the above
Answer:
c) Font colour
Question 137.
Using dialog box, all the formatting can be done at a single stretch with an online preview.
a) Paragraph
b) Character
c) Format
d) None of these
Answer:
b) Character
Question 138.
________ is the command to open Character dialog box.
a) Format → Character
b) Tools Character
c) Edit → Character
d) Format Paragraph
Answer:
a) Format → Character
Question 139.
The text can be changed to _____ case.
a) Uppercase
b) toggle case
c) sentence case
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
![]()
Question 140.
The text can be changed to ______ case,
a) Lowercase
b) Capitalize every word
c) sentence case
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 141.
The text can be changed to different case using ________.
a) Format Change case
b) Format → Case
c) Tools → Change case
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Format Change case
Question 142.
________ is used to draw attention to important information in a text.
a) Text editing
b) Highlighting
c) both A and B
d) None of these
Answer:
b) Highlighting
Question 143.
Highlighting can be removed by selecting the text and click ________ from the color palette.
a) No colour
b) No Fill
c) No background
d) None of these
Answer:
b) No Fill
Question 144.
After the formatting is applied, it can be removed by ________.
a) Ctrl + M
b) Ctrl + R
c) Ctrl + C
d) Alt + M
Answer:
a) Ctrl + M
Question 145.
A paragraph is any text that ends with a _______.
a) soft return
b) hard return
c) automatic return
d) none of these
Answer:
b) hard return
Question 146.
A hard return is accomplished anytime you press the key.
a) Insert
b) Enter
c) Backspace
d) Esc
Answer:
b) Enter
Question 147.
Paragraph _______ refers to the way in which the lines of a paragraph are aligned.
a) Alignment
b) justification
c) Adjustment
d) Both A and B
Answer:
d) Both A and B
Question 148.
_______ lets you control the appearance of individual paragraphs.
a) Paragraph Alignment
b) Soft return
c) Editing
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Paragraph Alignment
Question 149.
There are _______ types of alignment available in Open office Writer.
a) three
b) four
c) five
d) many
Answer:
b) four
Question 150.
________ is a paragraph alignment option.
a) Justify
b) Center
c) Left or Right
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 151.
_______ is the default alignment when a paragraph is typed.
a) Justify
b) Center
c) Left
d) Right
Answer:
c) Left
![]()
Question 152.
A paragraphs text is _______ aligned when it is aligned evenly along the left margin and uneven along the right margin.
a) Justify
b) Center
c) Left
d) Right
Answer:
c) Left
Question 153.
A paragraph’s text Is _______ aligned when it is aligned evenly along the right marign and uneven along the left margin.
a) Justify
b) Center
c) Left
d) Right
Answer:
d) Right
Question 154.
paragraphs text b _______ aligned, all the lines In the paragraph are alIgned to the canter of the page size.
a) Justify
b) Center
c) Left
d) Right
Answer:
b) Center
Question 155.
A paragraph’s text Is _______ aligned, all the lines In the paragraph, are arranged evenly both on the left and tight margins.
a) Justify
b) Center
c) Left
d) Right
Answer:
a) Justify
Question 156.
_______ alignment is achieved in writer by automatically inserting additional space between the words.
a) Justify
b) Center
c) Left
d) Right
Answer:
a) Justify
Question 157.
Paragraph formatting can be applied by _______ command.
a) Format → Character
b) Format → Paragraph
c) Format → Alignment
d) None of these
Answer:
b) Format → Paragraph
Question 158.
________ is the shortcut key to left align text.
a) Ctrl + L
b) Ctrl + R
c) Ctrl + J
d) Ctrl + E
Answer:
a) Ctrl + L
Question 159.
_______ is the shortcut key to right align text.
a) Ctrl + L
b) Ctrl + R
c) Ctlr + J
d) Ctrl + E
Answer:
b) Ctrl + R
Question 160.
_______ is the shortcut key to center align text.
a) Ctrl + L
b) Ctrl + R
c) Ctrl + J
d) Ctrl + E
Answer:
d) Ctrl + E
![]()
Question 161.
_______ is the shortcut key to justify align text.
a) Ctrl + L
b) Ctrl + R
c) Ctrl + J
d) Ctrl + E
Answer:
c) Ctrl + J
Question 162.
Line spacing determines the amount of _______ between lines of text in a paragraph.
a) vertical space
b) horizontal
c) Either A or B
d) None of these
Answer:
a) vertical space
Question 163.
By default, the lines are _______ spaced.
a) double
b) 1.5
c) single
d) None of these
Answer:
c) single
Question 164.
There are _______ different types of line spacing options.
a) seven
b) six
c) five
d) four
Answer:
a) seven
Question 165.
_______ dialog box is used to change the line space.
a) Character
b) Format
c) Paragraph
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Paragraph
Question 166.
_______ is the distance from the left and right margin of a paragraph.
a) orientation
b) Indent
c) header
d) footer
Answer:
b) Indent
Question 167.
_______ is used to improve the efficiency and readability of the paragraph and makes the paragraph look more attractive.
a) orientation
b) Indent
c) header
d) footer
Answer:
b) Indent
Question 168.
There are ________ types of indents.
a) six
b) five
c) four
d) three
Answer:
c) four
Question 169.
_______ is an indent type.
a) Left/Right indent
b) Hanging indent
c) First Line indent
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 170.
The _______ indent controls the space between the paragraph and the left margin.
a) Left
b) Hanging
c) First Line
d) Right
Answer:
a) Left
Question 171.
_______ is the default indent.
a) Left
b) Hanging
c) First Line
d) Right
Answer:
a) Left
![]()
Question 172.
Each click on the Increase indent icon moves the paragraph _______ inch away from the left margin.
a) 1
b) 1/2
c) 1 1/2
d) 2
Answer:
b) 1/2
Question 173.
The _______ indent controls the space between the paragraph and the right margin.
a) Left
b) Hanging
c) First Line
d) Right
Answer:
d) Right
Question 174.
Each click on the decrease indent icon ________ the indent applied by the Increase indent.
a) removes
b) adds
c) modifies
d) none of these
Answer:
a) removes
Question 175.
________ indentation indents the first line of the paragraph.
a) Left
b) Hanging
c) First Line
d) Right
Answer:
c) First Line
Question 176.
_______ indent is the most common way to start a new paragraph.
a) Left
b) Hanging
c) First Line
d) Right
Answer:
c) First Line
Question 177.
_______ is a special kind of indent where the first line of the paragraph alone hangs outside leaving the rest of the text.
a) Left
b) Hanging
c) First Line
d) Right
Answer:
b) Hanging
Question 178.
To apply Hanging indent, a value is _______ given in the “first line” option.
a) positive
b) zero
c) negative
d) none of these
Answer:
c) negative
Question 179.
_______ are used to emphasize list of things and make list easy to read and follow.
a) Bullets and Numbering
b) Paragraph alignments
c) Margins
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Bullets and Numbering
Question 180.
_______ provides an excellent way to segregate, list and organize information for a reader.
a) Bullets and Numbering
b) Paragraph alignments
c) Margins
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Bullets and Numbering
![]()
Question 181.
________ is a paragraph level attribute that applies a bullet character to the start of the paragraph.
a) Bullet
b) Numbering
c) Margins
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Bullet
Question 182.
_______ is suitable when the text has to be presented as a list of items preceded by a bullet symbol and no sequence has to be followed.
a) Bullet
b) Numbering
c) Margins
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Bullet
Question 183.
_______ attribute applies a numeral to the start of the paragraph.
a) Bullet
b) Numbering
c) Margins
d) None of these
Answer:
b) Numbering
Question 184.
_______ is more suitable when the text has to be presented as a sequence.
a) Bullet
b) Numbering
c) Margins
d) None of these
Answer:
b) Numbering
Question 185.
The numbers in a numbered list are updated automatically when we ________ paragraphs in the list.
a) add
b) remove
c) add or remove
d) none of these
Answer:
c) add or remove
Question 186.
_______ is a page formatting option.
a) margins and numbering
b) page layout
c) headers and footers
d) all the above
Answer:
d) all the above
Question 187.
Formatting document pages makes them _______.
a) look more attractive
b) easier to read
c) both A and B
d) none of these
Answer:
c) both A and B
Question 188.
The default page size in writer is .
a) 8.5″ x 11″
b) 11″ x 8.5″
c) 11.5″ x 8″
d) 8″x 11″
Answer:
a) 8.5″ x 11″
Question 189.
_______ margins are the white space around the top, bottom, left, and right of your document.
a) page
b) paragraph
c) text
d) document
Answer:
a) page
Question 190.
_______ margins let Writer know where to start placing the text at the top of a document.
a) Left
b) Right
c) Top
d) Bottom
Answer:
c) Top
Question 191.
_______ margins let Writer know, when to move on to the next page at the bottom,
a) Left
b) Right
c) Top
d) Bottom
Answer:
d) Bottom
![]()
Question 192.
_______ margins let Writer know where to start typing text on the left side
a) Left
b) Right
c) Top
d) Bottom
Answer:
a) Left
Question 193.
________ margins let Writer know where to stop and move to the next line on the right.
a) Left
b) Right
c) Top
d) Bottom
Answer:
b) Right
Question 194.
Changing or setting page margins in Open office writer can be done in ________ ways.
a) two
b) three
c) four
d) five
Answer:
a) two
Question 195.
________ is used to change the margins.
a) Ruler
b) Page style dialog box
c) both A and B
d) none of these
Answer:
c) both A and B
Question 196.
________ is used to change the margin when precise values are known.
a) Ruler
b) Page style dialog box
c) both A and B
d) none of these
Answer:
b) Page style dialog box
Question 197.
________ is used to change the margin when precise values are not known.
a) Ruler
b) Page style dialog box
c) both A and B
d) none of these
Answer:
a) Ruler
Question 198.
_______ refers to how the document will be displayed on screen and printed.
a) Margins
b) Page orientation
c) Header
d) Footer
Answer:
b) Page orientation
Question 199.
There are _______ different orientations.
a) two
b) three
c) four
d) five
Answer:
a) two
Question 200.
The width of the document is more than the height is called ________ orientation.
a) Portrait
b) Landscape
c) Ruler
d) None of these
Answer:
b) Landscape
Question 201.
_______ orientation is best suited for displaying professional photos, invitations, albums, tables etc.
a) Portrait
b) Landscape
c) Ruler
d) None of these
Answer:
b) Landscape
Question 202.
_______ is the most common and default orientation.
a) Portrait
b) Landscape
c) Ruler
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Portrait
![]()
Question 203.
The height of the document is more than the _______ width is called orientation.
a) Portrait
b) Landscape
c) Ruler
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Portrait
Question 204.
Books, newspapers will be displayed in ________ format.
a) Portrait
b) Landscape
c) Ruler
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Portrait
Question 205.
Changing the ________ color is not quite common.
a) text
b) page
c) both A and B
d) none of these
Answer:
b) page
Question 206.
Borders can be applied to _______.
a) an entire document
b) an entire page, paragraph
c) just to certain sections of the document
d) all the above
Answer:
d) all the above
Question 207.
The ________ is a section of the document that appears in the top margin.
a) header
b) footer
c) orientation
d) none of these
Answer:
a) header
Question 208.
________ displays the title or chapter name, author name of a document.
a) header
b) footer
c) orientation
d) none of these
Answer:
a) header
Question 209.
The ________ is a section of the document that appears in the bottom margin of the page.
a) header
b) footer
c) orientation
d) none of these
Answer:
b) footer
Question 210.
_______ displays the page number, date, time etc.
a) header
b) footer
c) orientation
d) none of these
Answer:
b) footer
Question 211.
In the header area, enter the text that is to be repeated in ail pages or Select _______.
a) Insert → Fields → Title
b) Insert → Header → Title
c) Insert → Fields → Header
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Insert → Fields → Title
Question 212.
________ command is used to insert page number in footer / header.
a) Insert → Fields → Page Number
b) Insert → Header → Page Number
c) Insert → Footer → Page Number
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Insert → Fields → Page Number
Question 213.
_______ is used to insert date in all the pages.
a) Insert → Fields →Date and Time
b) Insert → Header → Date
c) Insert → Footer → Date
d) Insert → Fields → Date
Answer:
d) Insert → Fields → Date
Question 214.
Once the headers and footers are given in the first page, the same text appears in – page(s).
a) all
b) first
c) specified
d) none of these
Answer:
a) all
![]()
Question 215.
_________ is the shortcut key to open the Find and Replace dialog box.
a) Ctrl + F
b) Ctrl + FI
c) Alt + F
d) Alt + Ctrl + F
Answer:
a) Ctrl + F
Question 216.
In Find and Replace dialog box, type the text you want to find in the _______ box.
a) Search for
b) Find for
c) Replace with
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Search for
Question 217.
In Find and Replace dialog box, type the new text in the ________ box.
a) Search for
b) Find for
c) Replace with
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Replace with
Question 218.
In Find and Replace dialog box, ________ button is used to find the next occurance of the word.
a) Find
b) Search
c) Find All
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Find
Question 219.
In Find and Replace dialog box, ________ button is used to find all the occurances of the word.
a) Find
b) Search
c) Find All
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Find All
Question 220.
In Find and Replace dialog box, ________ button is used to replace the current occurrence of the word.
a) Replace Once
b) Search
c) Replace
d) Change
Answer:
c) Replace
Question 221.
In Find and Replace dialog box ________ button is used to replace all the occurrences of the word.
a) Replace
b) Search
c) Replace All
d) Change All
Answer:
c) Replace All
Question 222.
While Find and Replace text, enable ________ to perform the search case- sensitively so that uppercase and lower cases are distinguished separately.
a) Match case
b) Whole words only
c) Both A and B
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Match case
![]()
Question 223.
While find and Replace text, enable _______ to make the search more specific to words used separately atone.
a) Match case
b) Whole words only
c) Both A and B
d) None of these
Answer:
b) Whole words only
Question 224.
The documents prepared using word processing software should be without any _______.
a) spelling mistakes
b) non-graphics
c) formatting
d) None of these
Answer:
a) spelling mistakes
Question 225.
To check the spelling of a document, OpenOffice includes a _______.
a) dictionary
b) spell check program
c) both A and B
d) none of these
Answer:
c) both A and B
Question 226.
OpenOffice writer check the spelling _______.
a) while typing
b) after typing
c) Both A and B
d) none of these
Answer:
Question 227.
_________ option checks each word as at is typed and displays a wavy red line under any misspelled words.
a) Auto spell check
b) Auto correct
c) Spell check
d) none of these
Answer:
c) Spell check
Question 228.
To perform a separate spelling check on the document (or a text selection) click the ________ button.
a) Auto Correct
b) Spelling and Grammar
c) Auto spell check
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Auto Correct
Question 229.
_______ checks the document or selection and opens the Spelling dialog box if any misspelled words are found,
a) Auto Correct
b) Spelling and Grammar
c) Auto spell check
d) None of these
Answer:
b) Spelling and Grammar
Question 230.
The dictionary language cart be changed to _______.
a) Spanish
b) French
c) German
d) All the above
Answer:
b) French
Question 231.
The new words can be added to a dictionary by clicking ______ button.
a) New
b) Include
c) Add
d) None of these
Answer:
d) None of these
Question 232.
Dictionaries also can be added or deleted through __________ directories.
a) custom
b) system
c) default
d) none of these
Answer:
a) custom
Question 233.
Auto Correct function has the facility to correct the _______ automatically.
a) common misspellings
b) typing errors
c) both A and B
d) none of these
Answer:
c) both A and B
Question 234.
_______ command is used to open the Auto Correct dialog box.
a) Tools → Auto correct
b) Format → Auto correct
c) File → Auto correct
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Tools → Auto correct
![]()
Question 235.
To stop the Writer to replace specific spellings, use Tools → Auto Correct, highlight the word pair and click ________ button.
a) Remove
b) Delete
c) Replace
d) None of these
Answer:
b) Delete
Question 236.
To add a new spelling to correct, type it into the Replace and With boxes and click – button.
a) Add
b) New
c) Replace
d) Insert
Answer:
Question 237.
Spell check identifies misspelled words and displayed with a _______ wavy line under the wrong word.
a) green
b) red
c) blue
d) yellow
Answer:
b) red
Question 238.
Spell check identifies the grammatical error and Is displayed with a _______ wavy line under the wrong word.
a) green
b) red
c) blue
d) yellow
Answer:
a) green
Question 239.
A _______ is a grid with a specified number of rows and columns.
a) spreadsheet
b) table
c) worksheet
d) none of these
Answer:
b) table
Question 240.
Tables can often be used as an alternative to _______ to organize materials.
a) spreadsheet
b) bullets
c) numbers
d) none of these
Answer:
a) spreadsheet
Question 241.
A table is a grid with a specified number of _______.
a) rows
b) columns
c) rows and columns
d) none of these
Answer:
c) rows and columns
Question 242.
_______ is used to insert a table.
a) Table → Insert → Table
b) Ctrl + F12
c) left-click the Table icon
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 243.
Formatting a table involves _______.
a) adding or removing rows or columns
b) merging and splitting cells
c) changing borders and the background
d) all the above
Answer:
d) all the above
Question 244.
Select the _______ option to define the first row in the table as the heading
a) Heading
b) Repeat Heading
c) Don’t split table
d) Border
Answer:
a) Heading
Question 245.
Select the _______ option to repeat the heading row if the table spans more than one page.
a) Heading
b) Repeat Heading
c) Don’t split table
d) Border
Answer:
b) Repeat Heading
Question 246.
Select the _______ option to prevent the table from spanning more than one page.
a) Heading
b) Repeat Heading
c) Don’t split table
d) Border
Answer:
c) Don’t split table
Question 247.
Select the _______ option to surround each cell of the table with a border.
a) Heading
b) Repeat Heading
c) Don’t split table
d) Border
Answer:
d) Border
Question 248.
_______ command is used to merge the cells in a table.
a) Table → Combine Cells
b) Table → Merge Cells
c) Table → Join Cells
d) Table → Integrate Cells
Answer:
b) Table → Merge Cells
![]()
Question 249.
______ command is used to split a cell in a table.
a) Table → Divide Cells
b) Table → Explore Cells
c) Table → Sub Cells
d) Table → Split Cells
Answer:
d) Table → Split Cells
Question 250.
To insert an image from a file in a document _______ command is used.
a) Insert → Picture → From File
b) Insert → Picture
c) Inserts Image → From File
d) Insert → From File → Picture
Answer:
a) Insert → Picture → From File
Question 251.
To insert a special character in a document _______ command is used.
a) Insert → Characters
b) Insert → Special Characters
c) Insert → Symbols → From File
d) Tools → Special Characters
Answer:
b) Insert → Special Characters
Question 253.
Auto Text allows you to assign to a key or key combination.
a) text
b) tables
c) graphics and other items
d) All the above
Answer:
b) tables
Question 254.
_______ is used to assign Auto Text.
a) Edit → Auto Text
b) Ctrl+F3
c) Either A or B
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Either A or B
Question 255.
________ is used to preview the document before printing.
a) File → Page Preview
b) Preview button
c) Both A and B
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Both A and B
Question 256.
In the page preview tool bar click ________ icon to display multiple pages.
a) Multiple Pages
b) Many Pages
c) More Pages
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Multiple Pages
Question 257.
To close the preview, click the ________ button.
a) Close Preview
b) Exit Preview
c) Navigate Preview
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Close Preview
Question 258.
________ is used print a document.
a) File → Print
b) Ctrl + P
c) Print Icon
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 259.
_______ is a print option.
a) All
b) Pages
c) Selection
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 260.
_______ is the shortcut key to double underline the text.
a) Ctrl + D
b) Ctrl + 2U
c) Ctrl + DU
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Ctrl + D
![]()
Question 261.
________ is the shortcut key for Redo Last Action.
a) Ctrl + X
b) Ctrl + Z
c) Ctrl + Y
d) Ctrl + R
Answer:
b) Ctrl + Z
Question 262.
_______ key move cursor with selection to the left.
a) Shift Left Arrow
b) Shift Right Arrow
c) Up Arrow
d) Down Arrow
Answer:
a) Shift Left Arrow
Question 263.
_______ key move cursor with selection to the right.
a) Shift Left Arrow
b) Shift Right Arrow
c) Up Arrow
d) Down Arrow
Answer:
b) Shift Right Arrow
Question 264.
_______ key move cursor to the beginning of the current word.
a) Shift Left Arrow
b) Shift Right Arrow
c) Ctrl + Left Arrow
d) Ctrl+ Right Arrow
Answer:
c) Ctrl + Left Arrow
Question 265.
_______ key move cursor to the end or the current word,
a) Shift Left Arrow
b) Shift Right Arrow
c) Ctrl + Left Arrow
d) Ctrl+ Right Arrow
Answer:
d) Ctrl+ Right Arrow
Question 266.
_________ is used for go and select from the beginning of line,
a) Shift + Home
b) Shift + End
c) Ctrl + Home
d) Ctrl+End
Answer:
a) Shift + Home
a) Shift + Home
Question 267.
______ is used for go and select fill the end.
a) Shift + Home
b) Shift + End
c) Ctrl + Home
d) Ctrl+End
Answer:
b) Shift + End
Question 268.
_______ key Is used for subscript,
a) Ctrl + Shift + B
b) Ctrl + Shift + P
c) Ctrl + Alt + B
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Ctrl + Shift + B
![]()
Question 269.
_________ key Is used for superscript,
a) Ctrl + Shift + B
b) Ctrl + Shift + P
c) Ctrl + Alt + B
d) Ctrl + Alt + P
Answer:
b) Ctrl + Shift + P
Question 270.
VIRUS means _______.
a) Vital Information Under Seize
b) Virtual Information Under Seize
c) Void Information Under Seize
d) Vital Information Urgent Seize
Answer:
a) Vital Information Under Seize
Part – II
Very Short Answers
Question 1.
What is word processor?
Answer:
Word processor is a computer software to create, edit, manipulate, transmit, store and retrieve a text document.
Question 2.
What do you mean by word processing?
Answer:
Word processing is an activity carried out by a computer with suitable software to create, edit, manipulate, transmit, store and retrieve text documents.
Question 3.
List popular proprietary word processing software along with their developers.
Answer:
Word Processing Package:
- Microsoft Word
- WPS Word
- WordPro
Developer:
- Microsoft Corporation
- Kingsoft
- Lotus Corporation
Question 4.
List popular open source word processing software along with their developers.
Answer:
Word Processing Package:
- OpenOffice Writer
- LibreOffice Writer
- Abiword
Developer:
- Apache
- The Document Foundation
- Abisource
Question 5.
What are the popular Tamil word processors?
Answer:
The familiar Tamil word processors are:
- Tamil OpenOffice writer
- Tamil LibreOffice writer
- Kamban 3.0
- Mentamizh 2017
![]()
Question 6.
What is Star Center?
Answer:
The opening screen of Open Office is called as “Star Center”.
Question 7.
How will you create a new document in OpenOffice?
Answer:
A new text document can be created by selecting File → New → Text Document from any OpenOffice Application. Ctrl + N keyboard short cut can also be used to open a new text document
Question 8.
How will you close a document?
Answer:
After the document is saved, it is still open. So, we can continue typing your document. When the work is finished, we should save the document and then dose document using File → Close command (or) Press Ctrl + W.
Question 9.
Write short note on opening an existing document.
Answer:
Once a document is saved, it can be opened at any time. To open an existing document, Click on the File → Open or Ctrl + 0, the Open dialog box appears, enter the name of the file in the File Name text box and click on OPEN button.
Question 10.
What are the different methods to type Tamil?
Answer:
Typing in Tamil has different methods,
- Using Tamil Font
- Using Tamil Interface.
Question 11.
What are the drawbacks of typing Tamil using Tamil font?
Answer:
Typing Tamil using Tamil font has some drawbacks:
- The user must be aware of Tamil typing.
- The particular font must be available in the system.
- It does not support other languages including English.
- The computer accepts characters as symbols not as language.
- It is not portable, i.e. if the document is sent to another computer, if the same font is not available; it is recognized as symbols not as original characters.
Question 12.
What are the advantages of typing Tamil using Tamil interface?
Answer:
The interface method provides the following advantages:
- It follows Unicode technique. Hence knowledge of Tamil typing is not necessary.
- It is easy to type documents in Tamil in any word processor.
- Some of the Unicode font§ like “Aria! Unicode” support all Indian languages including Tamil and English using respective language interface.
Question 13.
What is text editing?
Answer:
If there are some insertions or deletions in the typed document, it can be done while typing or after typing also. This operation is called text editing.
Question 14.
How corrections can be made in the document?
Answer:
Corrections can be made in two different ways:
- Backspace Key: Deletes the character left of the insertion pointer.
- Delete Key: Deletes the character right of the insertion pointer
![]()
Question 15.
What are the text selection methods?
Answer:
The text selection can be done by two methods:
- Selecting the continuous text.
- Selecting the non-continuous text.
Question 16.
How will you select the continuous text?
Answer:
To select the text continuously take the insertion pointer to the starting of the text and then hold the SHIFT key and drag the mouse across until the required text is selected and then release the SHIFT key.
Question 17.
How will you select the non-continuous text?
Answer:
To select the text not continuously, take the insertion pointer to the starting of the text and then hold the CTRL key and drag across it till the required text is selected and release the CTRL key.
Question 18.
Write note on DDE.
Answer:
Dynamic Data Exchange is a mechanism whereby the source data can be pasted into the destination as a linked, ‘live’ copy of the original. Any changes made in the source will immediately reflect into the destination.
Question 21.
What is font?
Answer:
A font is a set of characters in a particular style.
Question 22.
What is text formatting?
Answer:
Changing the default appearance of the text like changing the font type, size, color, style etc,, are called as Text formatting.
Question 23.
What is line spacing? What is default line space?
Answer:
Line spacing determines the amount of vertical space between lines of text in a paragraph. By default, the lines are single-spaced.
Question 24.
List the various line spacing options.
Answer:
The following are the line spacing options:
- Single
- 1.5 lines
- Double
- Proportional
- At least
- Leading
- Fixed
![]()
Question 25.
What is indentation? List its types.
Answer:
Indent is the distance from the left and right margin of a paragraph. There are four types of indents:
- Left Indent
- Right Indent
- First Line Indent
- Hanging Indent
Question 24.
What is the purpose of indenting text?
Answer:
It is used to improve the efficiency and readability of the paragraph and makes the paragraph look more attractive.
Question 25.
What is hanging indent?
Answer:
This is a special kind of indent where the first line of the paragraph alone hangs outside leaving the rest of the text. To apply Hanging indent, a negative value is given in the “first line” option of the paragraph dialog box.
Question 26.
What is the purpose of bullets and numbered text?
Answer:
Bullets and numbering are used to emphasize list of things and make list easy to read and follow. It provides an excellent way to segregate, list and organize information for a reader.
Question 27.
What are the page formatting elements?
Answer:
The page formatting elements are:
- Margins
- Numbering
- Page layout
- Headers
- Footers
Question 28.
What is the impact of page formatting?
Answer:
Formatting our pages makes them look more attractive and makes them easier to read.
Question 29.
What is page orientation? Mention its types.
Answer:
Page orientation refers to how the document will be displayed on screen and printed. There are two different orientations:
- Portrait
- Landscape
Question 30.
What is Landscape orientation? When it is used?
Answer:
- Landscape: The width of the document is more than the height.
- Purpose: This is best suited for displaying professional photos, invitations, albums, tables etc.
Question 31.
What is Portrait orientation? When it is used? Portrait:
Answer:
The height of the document is more than the width. This is the default orientation.
Purpose:
Normally books, newspapers will be displayed in this format.
![]()
Question 32.
How will you change the page orientation?
Answer:
To change the orientation:
- Select the page whose orientation is to be changed.
- In the Page style dialog box, under the Orientation group.
- Select Portrait or Landscape button.
Question 33.
What is header? What content may be included in the header?
Answer:
The header is a section of the document that appears in the top margin, which displays the title or chapter name, author name of a document.
Question 34.
What is footer? What content may be included in the footer?
Answer:
The footer is a section of the document that appears in the bottom margin of the page which displays the page number, date, time etc. which gets displayed on all the pages automatically.
Question 35.
How will you create header and insert header content?
Answer:
Inserting Header:
- Select Insert → Header → Default from the main menu.
- The header text area is separated from the normal text area.
- In the header area, Enter the text that is to be repeated in all pages or
- Select Insert → Fields → Title.
Question 36.
How will you create footer and insert footer content?
Answer:
Inserting Footer:
- Select Insert → Footer → Default from the main menu.
- Place the insertion pointer in the footer part of the page.
- Select Insert Fields → Date to insert date in all the pages.
Question 37.
How will you insert page number in header / footer?
Answer:
Once the Header / Footer area is enabled, the page numbers can be inserted by performing the following steps:
- Position the insertion pointer where you want to insert the page number
- Choose Insert → Fields → Page Number
- The page number appears with a gray background.
Question 38.
How will you change the page number style?
Answer:
Normally, the page numbers appear as 1,2,3 , To change the numbering style, the following sequence of steps can be performed:
- Position the cursor where the page number has to appear.
- Select Format → Page, which will bring the page style dialog box.
- Select Page Tab.
- Select the desired style and click OK button.
Question 39.
What are the tools for checking the spelling of a document?
Answer:
OpenOffice Writer includes a Dictionary and j Spell check program to check the spelling of a document.
Question 40.
What are the different ways to check the spelling of a document?
Answer:
OpenOffice Writer can identify the spelling mistakes as the document is typed or after the entire document is typed.
![]()
Question 41.
How will you turn off the auto correct?
Answer:
Auto Correct is automatically turned on. To turn it off, uncheck Format → Auto correct → While Typing.
Question 42.
How will you insert special character using auto correct?
Answer:
Auto Correct can be used as s quick way to insert special characters. For example, (c) will be auto corrected to (c). You can add your own special characters.
Question 43.
What is Table?
Answer:
A table is a grid with a specified number of rows and columns.
Question 44.
When table can be used in a document?
Answer:
Tables can often be used as an alternative to spreadsheet to organize materials. A well-designed table can help readers understand better what you are trying to convey.
Question 45.
How many methods are there to Insert a table in a document?
Answer:
There are two methods:
- Using Table Icon
- Using Insert Table dialog box
Question 46.
How wilt you open Insert Table dialog box?
Answer:
To open the Insert Table dialog box:
- Select Table → Insert → Table or
- Ctrl + F12 or
- left-click the Table icon
Question 47.
Write note on Formatting table.
Answer:
Formatting a table involves formatting of the table layout, formatting of the table text, adjusting the size of the table, its position on the page, adding or removing rows or columns, merging and splitting cells, changing borders and the background.
Question 48.
How will you merge the cells of a table?
Answer:
To merge a group of cells:
- Select the cells to merge.
- Right dick and choose Cell → Merge or choose Table → Merge Cells from the menu bar.
Question 49.
How will you insert a picture in a document?
Answer:
To insert an image from a file, the steps are as follows:
- Place the insertion pointer where you want the image to appear.
- Select Insert → Picture → From file.
- The insert picture dialog box appears where the picture gallery opens from which the desired picture can be selected.
- If the picture is not in the gallery, then browse the pictures from the folder, choose the desired one and
Click on the Open button - The selected picture is inserted into the document.
![]()
Part – III
Short Answers
Question 1.
Write about OpenOffice software.
Answer:
Open Office is the leading open-source office software suite for word processing, spreadsheets, presentations, graphics, databases and more. It is available in many languages and works on all common computers. It stores all our data in an International open standard format and can also read and write files from other common office software packages.
Question 2.
What are the packages available in OpenOffice software?
Answer:
OpenOffice is a productive office suite with a collection of different software packages such as
- OpenOffice Writer – Word Processor to create text documents.
- OpenOffice Calc – Spreadsheet to create worksheets.
- OpenOffice Base – Database
- OpenOffice Impress – Presentation software
- OpenOffice Draw – Drawing Software
- OpenOffice Formula – Create formula and equations
Question 3.
What are the important features of OpenOffice Writer?
Answer:
OpenOffice Writer provides these important features:
- Templates and styles.
- Page layout methods, including frames, columns, and tables.
- Embedding or linking of graphics, spreadsheets, and other objects.
- Built-in drawing tools.
- Master documents-to group a collection of documents into a single document.
- Change tracking during revisions.
- Database integration, including a bibliography database.
- Export to PDF.
Question 4.
How will you creating a new document in OpenOffice Writer ?
Answer:
A new OpenOffice Writer document can be created by various methods.
- From windows, select
- Start → All Programs → OpenOffice → OpenOffice Writer
From Star Center (Welcome Screen):
- Double-click on “OpenOffice” icon the desktop
- Now, a welcome screen appears as shown in the following figure

Question 5.
Write about control buttons in window.
Answer:
Control Buttons:
In the right corner of title bar, (1) minimize, (2) maximize/restore and (3) close control buttons are available as shown in the following figure.

Minimize button :
When we click Minimize button, it shrinks our document window smaller in size and shows it as a small button on the task bar. To restore it in its original size, click on the button, our document is restored to its original size.
Maximize button :
When we click Maximize button, our document window is displayed in full screen. When it is in full screen, the maximize button is changed as “Restore”.

When we click Restore button, the document window regains its original size.
Close button:
This button is called as “Close” button, when you click this button, the application is closed and OpenOffice returns back to the desktop. So, the red colored close button may be called as “Exit” or “Quit”.

There is another X mark on the right most corner of the menu bar. This is actually used to close your document. When we click this X mark, our document will be closed, OpenOffice will be still opened.
![]()
Question 6.
Explain Tool Bar available in OpenOffice Writer window.
Answer:
Under the menu bar, there are two toolbars available by default. They are:
- Standard Toolbar
- Formatting Toolbar
Standard Tool Bar:
This tool bar is just below the menu bar which consists of shortcut icons for frequently performed tasks. There are many shortcut icons like cut, copy, paste, undo etc…

Formatting Tool Bar: The formatting tool bar is below the standard tool bar which consists of icons used for formatting the text like bold, underline, italics, font type, font color etc.

Question 7.
Write short note on closing unsaved document.
Answer:
When we dose an unsaved file using the dose control button, Writer shows a warning message as shown in the following Figure.

If we accept the warning message, dick the “Save” button. When we click the “Save” button, it proceeds to save the file. If we are not willing to save the file, then click “Discard”, or if we want to cancel this warning and continue working in the same document click “Cancel”.
Question 8.
What are the text insertion modes?
Answer:
Insert Mode: To insert a text in between if something is left out, the insertion can be made by taking the insertion pointer to the current location and Press the Insert Key the newly typed text is inserted, so that the existing text moves to the right. This is Insert mode,
Type over mode: Press the Insert Key again, the text is over written on the existing text. This is called Type over mode. We can toggle between the insert mode and type over mode by pressing the Insert key.
Question 9.
Write the procedure to move text.
Answer:
To move a text from one location to another:
- Select the text to be moved
- Click Ctrl + X or Cut Icon or Edit → Cut
- The text is removed from the source location and placed in the clipboard
- Take the insertion pointer to the new location to be moved and
- Click Ctrl + V or Paste Icon or Edit → Paste
The required text Is moved to the required location.
Question 10.
Write the procedure to copy text.
Answer:
To copy a text from one location to another
- select the text to be copied
- Click Ctrl + C or Copy Icon or Edit → Copy
- A duplicate copy of the text is made and send to the clipboard.
- Take the insertion pointer to the new location to be copied and
- Click Ctrl + V or Paste Icon or Edit → Paste
The required text is copied to the required location.
Question 11.
Write Cut, Copy and Paste Icons and Shortcut keys.
Answer:

Question 12.
Explain Paste special option to copy text.
Answer:
Paste Special:
When we move or copy information, the paste option is used to send the information as a whole. But, to move or copy only some aspects of the data, like only it’s formatting or only value, the Paste Special option is used. To use the paste special, select the text and apply move or copy, then at the destination location.
- Click Edit → Paste Special (or) press Ctrl+Shift+V, or Alt+E+S the Paste Special dialog box opens
- The Paste Special menu varies depending upon the origin and formatting of the text (or object) to be pasted.
- Select DDE (Dynamic Data Exchange) link from the Paste special dialog box.
- Select the type of application and click on the OK button.
- The copied data is pasted into the document with a link.
Questions 13.
Explain Help system in OpenOffice Writer.
Answer:
Open Office Writer provides several forms of help. By pressing F1 or select Help from the menu bar the help window appears as shown in the following Figure.

- To activate tooltips, extended tips, and the help Agent, click Tools → Options → OpenOffice General.
- Enable Tips and Extended Tips check boxes.
- For a more detailed explanation, select Help → What’s This? and hold the mouse pointer over the icon where you want more help with.
![]()
Question 14.
What are the basic text formatting shortcuts?
Answer:

Question 15.
How will you change the text case? Explain. Changing Case
Answer:
Normally any text can be typed in upper or lower case. The text can be changed to different cases like:
- Uppercase (Capital letters)
- Toggle case (reverse case),
- Sentence case (first letter of each sentence Capital),
- Capitalize every word (first letter of each word capital),
- Lower case. (Small letters)
This can be done by:
- Select the text to change case
- Select Format → Change case and select the required one.
Question 16.
How will you change the fine space?
Answer:
Line spacing determines the amount of vertical space between lines of text in a paragraph. By default, the lines are single-spaced.
In Open Office, setting line spacing is quite easy through the context menu, select the line or word or phrase, right-click → line spacing, select the type single, 1.5, double etc. (OR)
- Select the entire document by
- Edit → Select All
- Format → Paragraph
- The paragraph dialog box appears, click Indents & Spacing tab
- In the line spacing option, select the type and click OK button.
Question 17.
How will you cancel or turning off bullets and numbering?
Answer:
The bullets and numbers can be removed easily.
- Select the text where the bullets and numbers are to be removed.
- Click on the bullets icon
 again to remove bullets.
again to remove bullets. - Click on the numbering icon
 remove numbering.
remove numbering.
Question 18.
How will you change the page size?
Answer:
The default page size in Writer is 8.5″ x 11″. However, for different types of documents, we may need to change the page size. To change the paper size:
- Select the page whose page size is to be changed.
- Select Format → Page, the page style dialog box appears.
- Select Page Tab.
- In the paper format group, select the format like A4, legal ……
- Or the width and height option can be used to set the page size.
Question 19.
How will you change page colour and borders?
Answer:
Changing Page colour:
Changing the page color is not quite common. To do so, in the Page style dialog box, select Background tab, In As option click on color and select the “color” from the color palette or select “graphic” to apply an image as a page background.
Changing borders:
Borders can be applied to an entire document, an entire page, paragraph, or just to certain sections of the document, From the Page style dialog box, select the Border tab, the user defined area helps to define the area of borders, the line style of borders, color of borders can be selected.
Question 20.
Write note on Auto spell check.
Answer:
Auto spell check option checks each word as it is typed and displays a wavy red line under any misspelled words. Once the word is corrected, the red wavy line disappears. This can be done through clicking the icon.
Question 21.
Write note on spell check program.
Answer:
Spell check is a software program that corrects spelling errors in word processing, email and documents. Spell check identifies and corrects misspelled words and the grammatical error is displayed with a green wavy line under the wrong word.
![]()
Question 22.
How will you insert rows/columns in a table?
Answer:
Inserting rows and columns: To insert rows or columns inside a table:
1. Place the insertion pointer in the row or in the column where we would like to add new rows or columns and right-click.
2. Choose Row → Insert – to insert a row or Column → Insert – to insert a column. A dialog box will appear, from which we can select the number of rows or columns to insert. We can also set the position of the new rows or columns to Before or After as shown in the following Figure.

Question 23.
How will you delete rows and columns in a table?
Answer:
To delete rows or columns inside a table:
- Place the insertion pointer in the row or column to be deleted and right-click,
- Choose Row → Delete – to delete a row or Column → Delete – to delete a column.
- The selected row / column is deleted.
Question 24.
How will you split a cell in to more than one in a table?
Answer:
To split a cell:
1. Place the insertion pointer inside the cell.
2. Right click and choose Cell → Split, or choose Table → Split Cells from the menu bar.
3. Select the direction of the split, horizontally (for rows), or vertically (for columns), as well as the total number of cells to create.

Question 25.
How will you insert special characters in a document?
Answer:
Inserting Special Characters:
Many symbols which are used in a mathematical equation like alpha(α), beta(ß), pi(π) etc., are not available on the standard keyboard. To insert such characters, the procedure given below is followed:
- Place the insertion pointer in your document where you want the character to appear.
- Click on the Insert → Special characters.
- The Special characters dialog box appears from which the desired symbol can be selected by clicking on the character.
- As we select each character, it is shown on the lower right, along with the numerical code for that character
- If we do not find a particular special character we want, try changing the font selection.
- Click the OK button and the character is inserted at the current location.
Question 26.
Explain document preview before printing. Preview the document to be printed
Answer:
It Is a good practice to preview the document before taking the print out. The steps to be followed to preview the document:
- Click File → Page Preview/, or click the Page Preview/ button. The Writer displays the Page Preview toolbar
- In the page preview tool bar dick Multiple Pages Icon to display multiple pages.
- To close the preview, click the Close Preview button.
Question 27.
How will you print a document with printer settings?
Answer:
The following are the steps to change the printer setting :
1. Click File → Print or Ctrl + P or Print File Icon which opens the Print dialog box as shown in the following Figure.

2. Click General Tab.
3. Select the required printer from the list of printers.
4. Under Range and copies section : select All Pages option to print all pages, select Pages option to specify the particular page or page range.
5. Specify Number of Copies using spin arrows.
6. Click Print button.
Part – IV
Explain In Brief
Question 1.
Draw and explain the parts of OpenOffice writer window.
Answer:
The following figure shows the contents of OpenOffice Writer window such as Title bar, Menu bar, Standard Toolbar, Formatting Tool bar, Ruler, Work space and Status bar. The components of a openoffice writer window are explained below the figure.

Title Bar:
The title bar is displayed at the top most part of the window, which displays the name of the document and the name of the application. By default, the initial document is given the name as Untitledl.
Control Buttons: In the right corner of title bar, (1) minimize, (2) maximize/restore and (3) close control buttons are available
Menu Bar: The menu bar is just below the title bar which comprises of various menus consisting of various options.
Tool Bar: Under the menu bar, there are two toolbars available by default.
They are:
(1) Standard Toolbar
(2) Formatting Toolbar
Ruler:
The ruler is a scale below the formatting tool bar which shows the margins. There are two set of rulers (1) Horizontal ruler and (2) Vertical ruler. Horizontal ruler is used to set left and right margins of a page and vertical ruler for top and bottom setting.
Work Space :
The work space is the blank area which is used to type the content of the file, A flashing vertical bar appears at the beginning of the screen which is called as “Insertion pointer”.
Status Bar:
The status bar is at the bottom of the window which shows the current status of the document such as number of pages, current page number, default language etc.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain various menus in the menu bar.
Answer:
Menu Bar:
The menu bar is just below the title bar which comprises of various menus consisting of various options.
![]()
File : The File menu contains various option for file management tasks: New, Open, Close, Save, Save As, Print, Export etc.
Edit: The Edit menu contains the editing options like, cut, copy, paste, Undo, Redo etc.
View: The View menu contains the options which are used to modify the environment of writer like display of toolbars, web layout, print layout, navigator etc. ,
Insert: The Insert menu contains commands for inserting various elements such as pictures, tables, charts, comments, headers, footers, special characters etc.
Format : The Format menu contains the options of various text and page formatting features like page size, layout, font characteristics, bullets and numbering etc.
Tables : The Table menu contains various tools to manage and manipulate tables such as create table, insert rows, insert columns, split cells, merge cells etc.
Tools: The Tools menu contains various tools and functions such as spell check, macros, mail merge, end notes/footnotes etc.
Window : The window menu shows display options such as New Window, Close Windows, Split and Freeze.
Help : The Help menu lists out the inbuilt help features available with OpenOffice.
Question 3.
What are the various shortcut keys to move easily within the document?
Answer:
There are different ways of moving within a document. There are many shortcut keys given in the following Table which are used to move easily within a document.

Question 4.
Explain the different methods of selecting the text.
Answer:
Selection using Mouse:
To select the text using mouse:
- Take the insertion pointer to the start of the text.
- Hold down the Left mouse button and drag it across the text.
- Release the mouse button when the required portion of text is selected.
- The selected text will be highlighted.
Selection using Keyboard:
- Take the insertion pointer to the start of the text.
- Hold the Shift key and use the movement keys to drag across the required portion.
- When the required portion is selected release the Shift key.
- The selected text will be highlighted.
Selection using Shortcut keys:
- Shortcut keys help to select the text quickly and easily.
- To select a word – Double dick on the word
- To select the entire document – Press Ctrl + A
Question 5.
What are the font formatting options? Explain.
Answer:
a) Changing font type: The default font type is Times New Roman and the type of font can be changed by clicking on the Font Type icon
b) Changing font size: The default size of font is 12 points which can be changed by clicking on the Font Size icon
c) Changing font colour: The default font color is black and the font color can be changed by clicking on the Font colour icon which shows the color palette from which the required color can be selected. The other formatting Options can be selected by using Format → Character.
The Character dialog box is displayed as shown in the following Figure using which ail the formatting can be done at a single stretch with an online preview.

Question 6.
Explain the various paragraph alignments. Paragraph Alignment
Answer:
A paragraph is any text that ends with a hard return. Paragraph Alignment refers to the way in which the lines of a paragraph are aligned. There are four types of alignment available in Open office Writer – left – alignment, Right – alignment, Center – alignment, and Justify – alignment.
Left-alignment: A paragraph’s text is LEFT aligned when it is aligned evenly along the left margin and uneven along the right margin. This is the default alignment when a paragraph is typed.
Right-alignment: A paragraph’s text is RIGHT aligned when it is aligned evenly along the right margin and uneven along the left margin.
Center-alignment: All the lines in the paragraph are aligned to the center of the page size.
Justified-alignment: All the lines in the paragraph, are arranged evenly both on the left and right margins. This is achieved in writer by automatically inserting additional space between the words.
Paragraph formatting can be applied by Format → Paragraph, the paragraph dialog box appears as displayed in the following Figure.

The paragraph formatting can also be done by icons using the formatting tool bar as shown in the following Figure and shortcut keys as shown in the following Table.
![]()
Paragraph Alignment Icons and shortcut Keys

An example showing all the four paragraph alignment:
Left Aligned Text: All power is with in you take up one idea, make that one idea your life. Think of it dream of it, live on that idea let the brain, muscles, nerves, every part of your body be full of that idea.
Right Aligned Text: All power is with in you take up one idea, make that one idea your life. That of it dream of it, live on that idea let the brain, muscles, nerves, every part of your body be full of that idea.
Center Aligned Text: All power is with in you take up one idea, make that one idea your life. Think of it dream of it, live on that idea let the brain, muscles, nerves, every part of your body be full of that idea.
Justified Aligned Text: All power is with in you take up one idea, make that one idea your life. Think of it dream of it, live on that idea let the brain, muscles, nerves, every part of your body be full of that idea.
Question 7.
What is indenting text? Explain the various methods.
Answer:
Indent is the distance from the left and right margin of a paragraph. It is used to improve the efficiency and readability of the paragraph and makes the paragraph look more attractive. There are four types of indents:
- Left Indent
- Right Indent
- First Line Indent and
- Hanging Indent
Left indent: The Left indent controls the space between the paragraph and the left margin. This is the default indent. Each click on the Increase indent icon moves the paragraph Vi inch away from the left margin.
The left indent can also be applied by Format → Paragraph → Indents & Spacing tab, enter a value in the “before text” spin box. This results in a left indent.
Right Indent: The Right indent controls the space between the paragraph and the right margin. Each click on the decrease indent icon removes the indent applied by the Increase indent. The Right indent can be applied by the dialog box method. Select Format → Paragraph → Indents & Spacing tab, enter a value in “after text” spin box. This results in a right indent.
First Line Indent: A first-line indentation indents the first line of the paragraph. It is the most common way to start a new paragraph. This indent can be applied by Format → Paragraph → Indents & Spacing tab, select first line option in the Indent group, enter a positive value which results in first line indent.
Hanging indent: This is a special kind of indent where the first line of the paragraph alone hangs outside leaving the rest of the text. To apply Hanging indent, a negative value is given in the “first line” option of the paragraph dialog box.
Example:

![]()
Question 8.
Explain Bullets and Numbering text with suitable example.
Answer:
Bullets and numbering are used to emphasize list of things and make list easy to read and follow. It provides an excellent way to segregate, list and organize information for a reader.
Bullets: This is a paragraph level attribute that applies a bullet character to the start of the paragraph. In bulleted lists, each paragraph begins with a bullet character.
This is suitable when the text has to be presented as a list of items preceded by a bullet symbol and no sequence has to be followed. Bullets are quickly created by clicking on the bullet icon ![]()
Numbering : This attribute applies a numeral to the start of the paragraph. Numbering is more suitable when the text has to be presented as a sequence. In numbered list, each paragraph begins with an expression that includes a number or letter and a separator such as a period or parenthesis.
The numbers in a numbered list are updated automatically when we add or remove paragraphs in the list. Numbering is quickly created by clicking on the numbering icon ![]() .
.
Style of Bullets and Numbering:
The default type of bullet is ( . ) and the default type of numbering is (1, 2, 3 …. ). The style of bullets and numbering can be changed by applying the following steps:
- Select the text to be bulleted
- Format → Bullets and Numbering
- Select Bullets Tab
- The Bullets and Numbering dialog box appears where different styles of bullets are displayed
- Click on the required style
- Click Ok button
- The selected text is bulleted.
Example:
- CHENNAI
- MADURAI
- TIRUNELVELI
To apply Numbering:
- Select the text to be numbered
- Format → Bullets and Numbering
- Select Numbering Type Tab
- The Bullets and Numbering dialog box appears where different styles of numbering are displayed
- Click on the particular style
- Click Ok button
- The selected text is numbered.
Example:
- CHENNAI
- MADURAI
- TIRUNELVELI
Question 9.
Explain the methods of changing page margins.
Answer:
Page margins are the white space around the top, bottom, left, and right of your document. Margins let Writer know where to start placing the text at the top of a document, when to move on to the next page at the bottom, where to start typing text on the left side, and where to stop and move to the next line on the right.
Changing or setting page margins in Open office writer can be done in two ways:
- Using the Rulers – quick and easy, but does not have precise values.
- Using the Page Style dialog box – can specify precise values for the margins.
Changing Page Margins – using Ruler
- The shaded sections of the rulers are the margins.
- Hold the mouse pointer over the line between the gray and white sections.
- The mouse pointer turns into a double-headed arrow.
- Hold down the left mouse button and drag the mouse to move the margin and release it at the required point.
- The new margin is set.
Changing Page Margins – using the Page Style dialog box:
To change margins using the Page Style dialog box
- Right-click anywhere on the page and select Page from the popup menu and select page tab of page style dialog box.
- In the Margins boxes, specify the values for left, right, top and bottom margins.
- Click on ok button.
Question 10.
What is meant by Automatic correction? How will you add an entry in the Auto correct list.
Answer:
Auto Correct function has the facility to correct the common misspellings and typing errors, automatically. For example, “hte” will be changed to “the” which can be done through the menu option, Tools → Auto Correct to open the Auto Correct dialog box which provides the chance to change the misspelled word by a default name.
1. To stop the Writer to replace specific spellings, use Tools → Auto Correct, highlight the word pair and click Delete.
2. To add a new spelling to correct, type it into the Replace and With boxes and click New.

Procedure to add an entry in Auto correct list:
The following steps to correct the word “computer” into “computer” automatically by adding entry in the auto correct list.
- Goto Tools → Auto correct Options
- Click the Replace tab and type “computer” in Replace text box and “computer” in With text box. Then Click OK.
- The word “Computer” is replaced with “Computer” and displayed in the list.
- After entering this, when you type “computer” in the document, it will be automatically changed to the correct spelling “computer”.
![]()
Question 11.
Explain the different methods of inserting a table in a document.
Answer:
There are two methods to create a table :
1. Using Table Icon ![]() To insert a table quickly from the standard tool bar:
To insert a table quickly from the standard tool bar:
- Place the insertion pointer where we want the table to appear.
- Click the arrow to the right side of the Table icon.
- In the drop down grid, select the number of rows and columns for the table.
- The table will appear at the location of our insertion pointer.
2. Using Insert table dialog box – Select Table → Insert → Table or Ctrl + F12 or left-click the Table icon. From the dialog box, we can:
- Select the number of rows and columns of the table.
- Give a Name to the table to later distinguish it in the Navigator.
- Select the Heading option to define the first row in the table as the heading.
- Select the Repeat heading option to repeat the heading row if the table spans more than one page.
- Select the Don’t split table option to prevent the table from spanning more than one page.
- Select the Border option to surround each cell of the table with a border.

The Auto Format button at the bottom of the dialog box opens the Auto Format dialog box. From here it is possible to choose among different predefined formats.
Questions 12.
How will you insert shapes in a document by drawing it?
Answer:
Inserting Shapes:
OpenOffice writer uses the drawing tools, to create various shapes by using the Drawing toolbar. The drawing tool bar can be obtained by clicking View → Toolbars → Drawing as displayed on the following Figure.

To use a drawing tool, the steps are as given below:
- Click In the document where we want the drawing to be anchored.
- Select the Tool from the Drawing toolbar as shown in the above Figure. The mouse pointer changes to a drawing-functions pointer.
- Move the cross-hair pointer to the place in the document where we want the graphic to appear and then click-and-drag to create the drawing object.
- Release the mouse button. The selected drawing function remains active, so we can draw another object of the same type.
- To cancel the selected drawing function, press the Esc key or dick on the Select icon on the Drawing toolbar.
Question 13.
Explain Auto Text in detail.
Answer:
Inserting Auto Text: Auto Text allows you to assign text, tables, graphics and other items to a key or key combination. For example, rather than typing “TamilNadu” every time you use that phrase, we might just type “tn” and press F3. We can also save a formatted Tip as Auto Text and then insert a copy by typing “tip” and pressing F3.
To assign Auto Text shortcut to some text, the steps are as follows:
- Type the text into our document.
- Select the text so that it is highlighted.
- Select Edit → Auto Text (or press Ctrl+F3).
- Enter a name for our shortcut. Writer will suggest a one-letter shortcut, which you can change.
- Click on the inverted arrow of the Auto Text button on the right and select New (text only) from the menu.
- Click Close to return to our document.
- Once the entry is created, to insert the auto text into the document, place the cursor where the text is to be inserted and dick Ctrl+F3,
- Select the name from the list of entries and click Insert button.
- The auto text is inserted into our text.












































































 is the logo of ________ OS
is the logo of ________ OS is the logo of ________ OS
is the logo of ________ OS is the logo of ________ OS.d
is the logo of ________ OS.d is the logo of ________ OS
is the logo of ________ OS is the logo of ________ OS
is the logo of ________ OS is the logo of ________ OS
is the logo of ________ OS








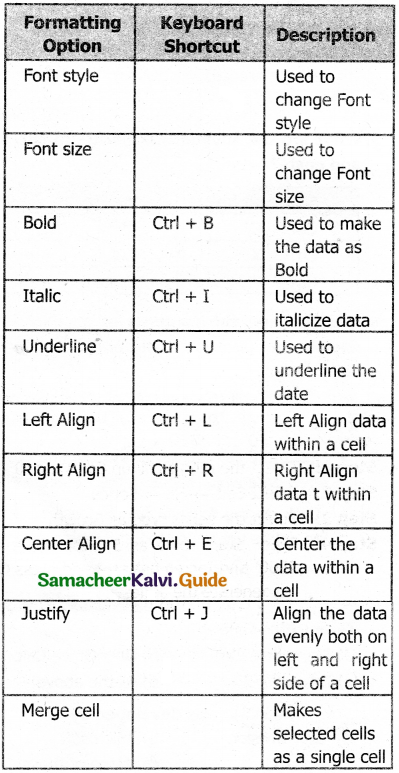








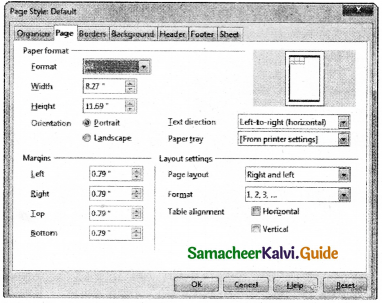



































































 For the surface μ = 0.4, The work done by applied force, frictional force and net force are
For the surface μ = 0.4, The work done by applied force, frictional force and net force are


































































































